How a Company Can Measure the Maturity of the Dark Web Intelligence Program
Cyber Threat Intelligence

Context of the Blog Post
When conducting research on the dark web, specific legal, regulatory, and political risks are not present in other types of research. Risks still exist even if analysts and intelligence companies present their work as research. That is why it is important to establish policies and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) to reduce the risks to the analyst, their company, and their clients. Resecurity is experienced in helping customers develop a research strategy that will enhance the impact of their company, protect their products, services, and customers, and reduce the risk of collecting these unique insights.

Who Should Read This Post?
This blog post is intended for managers and analysts responsible for protecting their company and employees from cybercrime. Whether new to this field or an expert, you can learn about potential metrics relevant to your efforts.
Key Takeaways
- The risks of researching on the dark web differ from other types of research. Legal, regulatory, and political risks must be considered when analyzing the dark web.
- Resecurity can help companies define an appropriate dark web research maturity model and develop policies and procedures for utilizing dark web intelligence to safeguard their products, services, customers, employees, and company IP.
- Every company should have a target maturity score that suits its unique resources, risks, tolerances, and legal/regulatory requirements. Each company’s ultimate objective is to achieve a target maturity score appropriate for itself.
- The list of variables in this blog may need to be adapted for an individual company. Our goal with this blog is to assist companies in creating a tailored list of variables pertinent to their specific needs.
- As with most other research, dark web research must be agile and responsive to potential threats while being mindful of budget resources. Standardized processes such as SOPs, research briefs, and review processes can improve the efficiency of dark web research requests.
- Resecurity aims to provide a framework for companies to assess the maturity of their dark web intelligence research. However, it is not intended to offer legal advice but to guide companies in creating their policies and SOPs.
Related information
Dark Web Research is a Critical Component of Threat Intelligence and Cybersecurity.
The Variables To Measure a Company’s Maturity Level.
Together these variables can be used by a company to create an appropriate maturity model for dark web research.
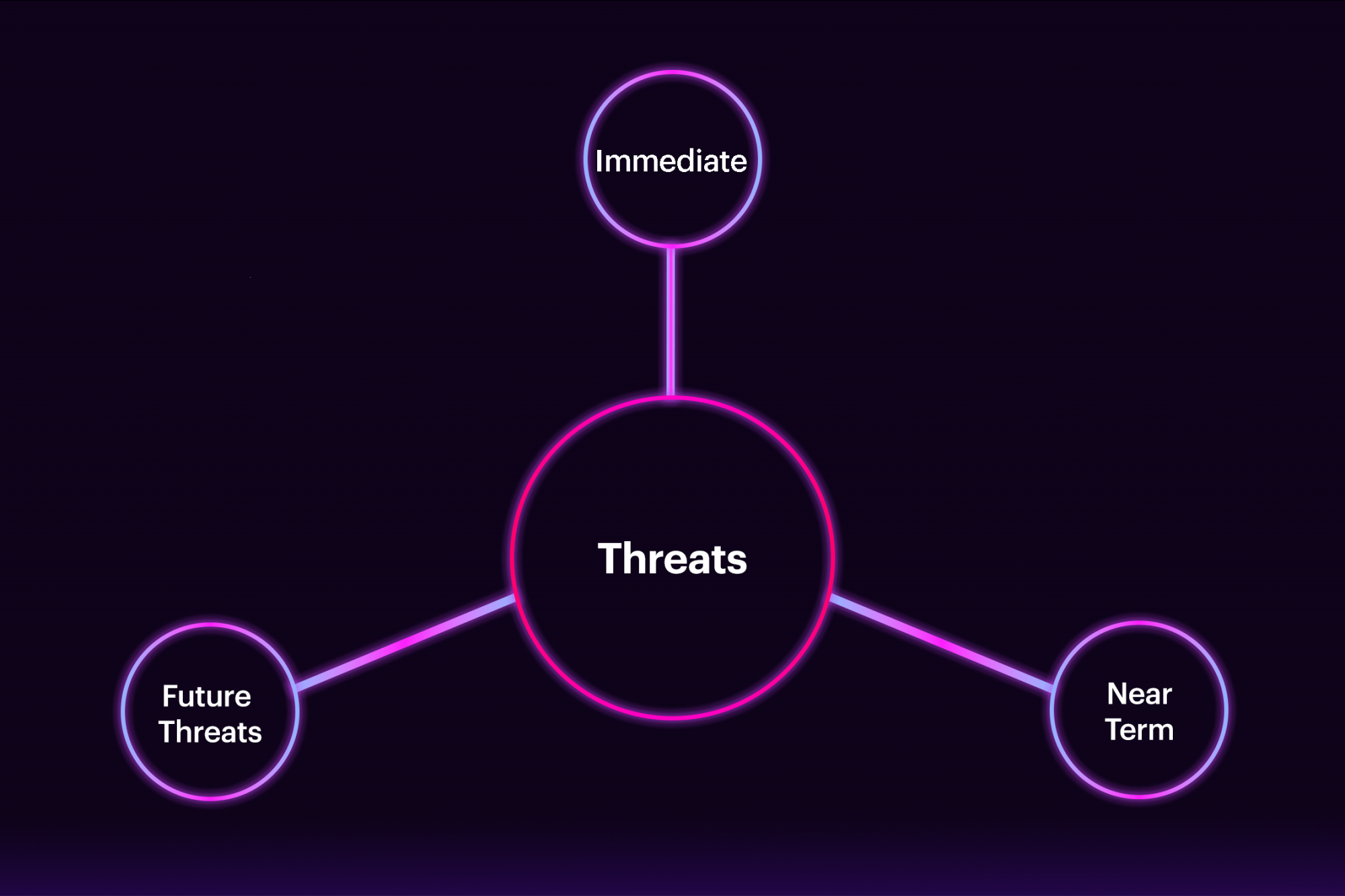
Forward-Looking Threat Intel
Often, threat intel focuses on current or near-term threats (1–30 days) rather than on future threats (30+ days). Even though contemporary and near-term are essential, focusing on future threats better allows a company to position its security posture to thwart future threats before they become real.

Cross-Team Collaboration
To effectively conduct threat intelligence on the dark web, it’s important to have institutional knowledge. While it’s typically done to support a specific team’s objectives, it’s best to centralize the process so that all teams in the company can benefit. Some companies have one group responsible for collecting and sharing threat intelligence, while others centralize auditing and oversight, even if the intelligence collection is decentralized. Both approaches are acceptable but should align with the company’s culture and governance.

Points of Failure
Intelligence collection has several potential points of failure. These may include relying on a single source for dark web intelligence, having only one employee with expertise in designing and conducting such intelligence, and having limited capacity to handle alerts generated from dark web intelligence efforts.
Oversight
At a minimum, there is a need for at least one employee skilled in designing, conducting, or managing various dark web research projects. Ideally, a company should have multiple individuals with sufficient expertise to oversee and advise analysts and teams on their dark web intelligence effort. Developing this level of knowledge takes time, but mature dark web intelligence efforts can make it easier for someone to acquire.
Companies must have a team (or a distributed team) of skilled employees who can analyze tips from dark web research to combat cybercrime and mitigate cyber threats. An intelligence vendor or internal analysts can do this research. The company should decide whether to separate dark web research and tip analysis duties if the latter conducts the investigation. Multiple individuals with expertise in these areas are necessary to ensure the successful management of tips from third parties. This will prevent any single point of failure and guarantee sufficient language and subject matter knowledge. For multinational companies, the fight against cybercrime requires consistent effort outside of typical work hours.
Intelligence Vendors
It is difficult for any single intelligence vendor to provide a complete understanding of the criminal ecosystem. Using multiple vendors is often necessary for better visibility, which can increase costs and complexity. Alternatively, companies can use a combination of internal analysts and dark web intelligence vendors. It’s essential to ensure that if multiple vendors or analysts conduct similar research, the company works with them to avoid potential overlap and have a process for deconfliction. Every dark web intelligence vendor has their area of expertise, language coverage, and research capabilities. Hence, a company must find the right vendor(s) to meet its requirements when collecting intelligence from the dark web.
Documented Processes in Place
When researching on the dark web, a company must ensure that its analysts follow proper procedures and do not act impulsively. Failure to do so can seriously affect the analyst, their colleagues, and the company’s customers. It is recommended that SOPs be established for research on the dark web.
- Establishing clear guidelines for the types of forums that analysts can enter is essential. For instance, should analysts resort to illegal means to gain access to a forum? Also, should analysts access dark web forums known or suspected of engaging in criminal or illicit activities? These are questions that must be carefully considered.
- What are the differences between the capabilities of company analysts and intelligence vendors? While company analysts may have certain authorized activities, intelligence vendors often have more comprehensive abilities. For instance, intelligence vendors possess the necessary operational security to procure a crime kit for a customer, which includes research to confirm that the seller is not embargoed.
- To properly plan a research project, creating a research brief is essential. The brief should outline the specific research questions, desired outcomes, and how the results will be communicated. When creating a research brief, it’s essential to include the estimated cost and timeframe of the project, as well as any identified risks and how to mitigate them. The brief should also define the project’s acceptable fidelity and tolerance for false positives/negatives. Additionally, any conditions for company analysts or third parties involved in the research should be specified. While it’s not required, it’s also helpful to consider the potential impact of the expected insights.
- When collecting data from the dark web, it’s essential to establish proper data governance procedures. Such data often contains sensitive information like individual PII and company IP. To ensure safety, a company must have processes to remove harmful content, control access to the data while in possession, and define policies for reporting any data that impacts a third party. Additionally, the company should destroy the data when it’s no longer needed.
- Suppose an analyst comes across CSAM while researching the dark web. Even though the risk is very low, accidental access can occur. Many countries require anyone who discovers CSAM to report it to a specific authority. To prepare for such an event, the company should have a policy for analysts to follow and support processes to help them deal with any exposure to such material. Additionally, any employee who may encounter offensive videos, audio, images, etc., should sign a document acknowledging the potential exposure. This will help the company set expectations and avoid creating a hostile work environment.
Repeatable Results, Enforced by Documented Processes
Using SOPs for dark web research can help a company establish consistent and repeatable processes. These processes can provide multiple benefits, including easier reporting.
- Conducting research becomes less costly and risky with this approach.
- Using consistent processes and measurements in research over time is important to ensure accuracy. This prevents discrepancies in insights due to changes in the dark web ecosystem or inconsistencies in research methodology.
Auditable
While having processes, policies, and SOPs in place is beneficial for a company, it is essential to have a system for auditing the compliance of analysts. Additionally, any intelligence vendor must be auditable to ensure they accurately follow the conditions outlined in the PO/SOW.
Cost-Effective
When there are limitations in resources and budget, outsourcing research can be a more economical option compared to relying only on internal resources. This may involve expenses but can aid in meeting budget projections and satisfying customer demands. Nonetheless, additional information is needed to understand the matter thoroughly.

Innovation
A company can gather information on potential research projects and expected insights if it wants to research the dark web. This can be achieved by referring to past research projects, consulting with third-party intelligence vendors and industry partners, and attending relevant research conferences. However, if the company needs to conduct new and unique research, it will require a process for conducting precedent-setting research.
Areas of Focus
When conducting research, companies may focus on various areas, such as monitoring specific geographic and language coverage or forums that specialize in different types of cybercrime. It’s important to understand that the dark web is not a single entity but rather a fragmented ecosystem, with different barriers to analysts. Language is a particularly complex area of focus, as different forums may use different languages and have their own jargon, dialects, and slang. Relying on machine translation or non-native speakers to understand the content posted on the dark web can be problematic and will reduce the chances of success.
Feedback Loop
Continuous improvement in the impact of dark web research projects is ensured through feedback loops. This helps ongoing projects to improve over time. Feedback on the impact, successful and unsuccessful tactics, and areas for improvement in future projects must be collected and managed by the dark web research team. The feedback should come from the teams who consumed the research, the analysts, and the third-party researchers.


Nimble and Quick to Respond
As with most other research, dark web research must be agile and responsive to potential threats while being mindful of budget resources. Standardized processes such as SOPs, research briefs, and review processes can improve the efficiency of dark web research requests.
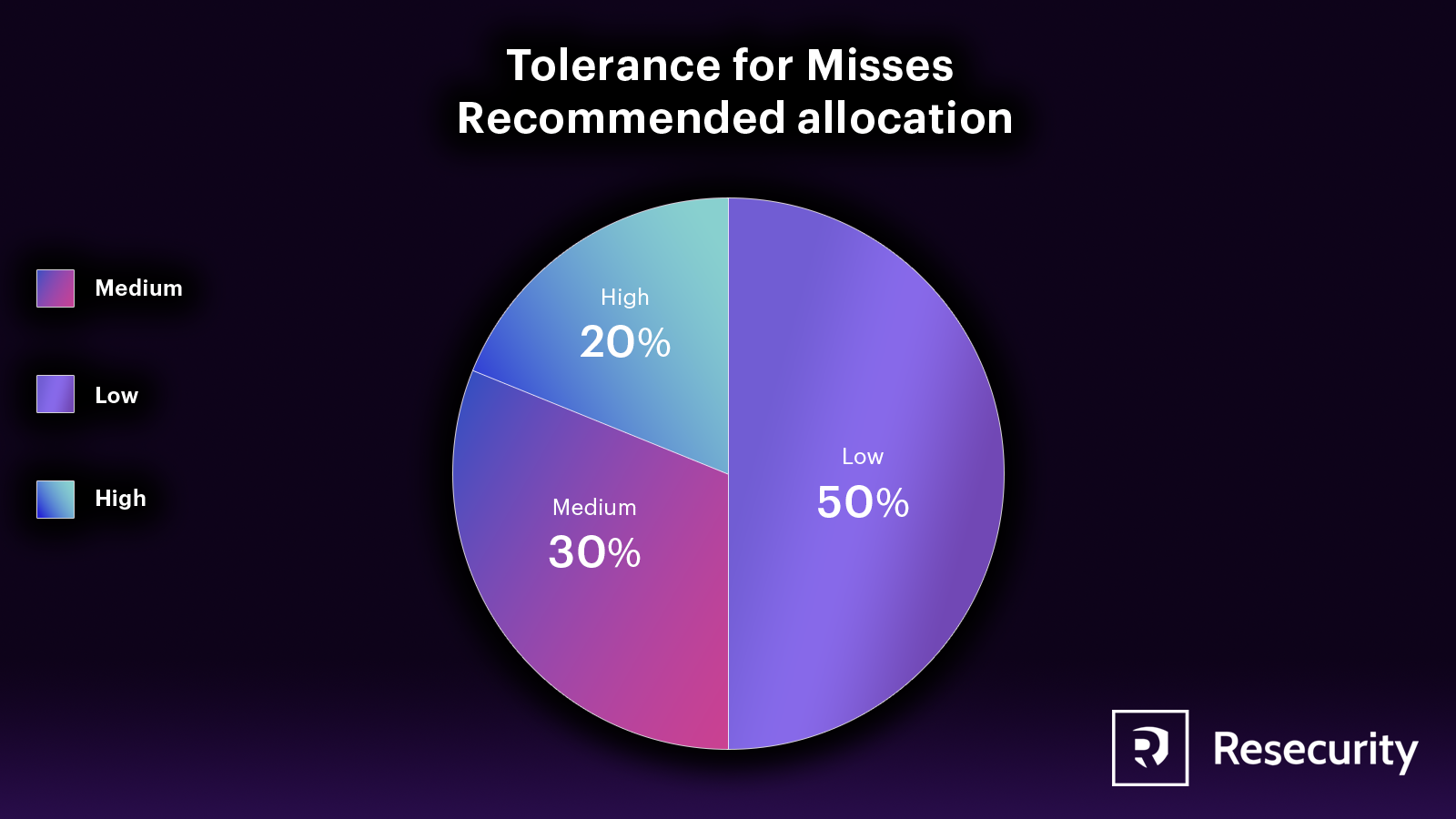
Tolerance for Misses
When researching on the dark web, it's crucial to balance adhering to SOPs and being flexible enough to handle unforeseen situations in an appropriate timeframe. The ideal balance will depend on budget, available resources, and time constraints, which should be outlined in the project's research brief. To ensure consistency across all projects, the company should establish clear guidelines and have a system for documenting and updating SOPs as needed, especially in unexpected circumstances.
The Process to Triage Ad Hoc Tips
Sometimes, valuable information from the dark web is found unexpectedly and not as part of a research project. This information may include compromised credentials, signs of a breach, vulnerable software, or a third-party supplier or distributor being breached. To address these tips effectively, a company should have a process to assess and prioritize them quickly. If the information is confirmed to be significant, the dark web research team should pass it to the relevant team or entity and help mitigate the problem.

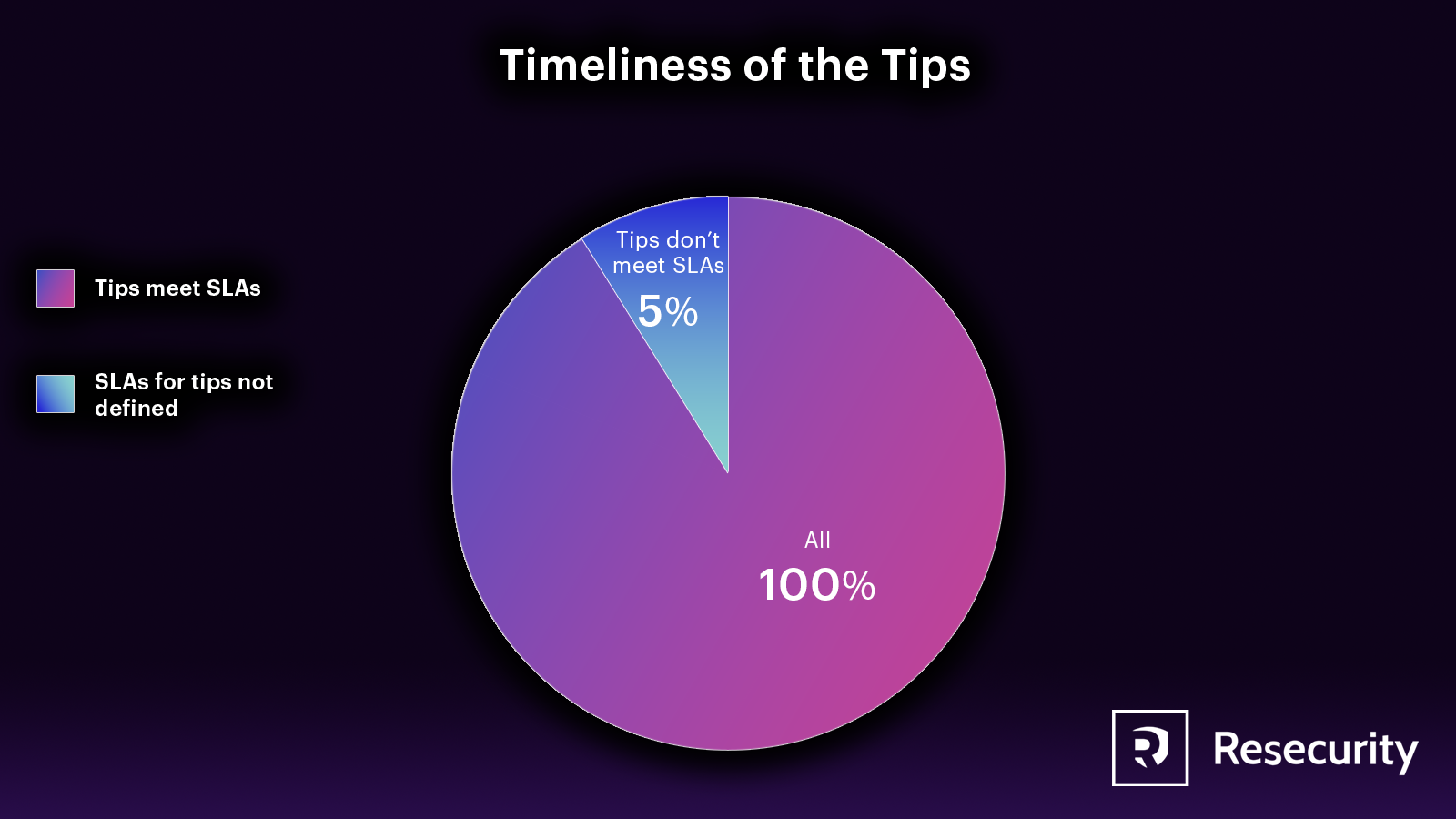
Timeliness of the Tips
Getting tips is great, but ensuring they are timely and credible is essential. To do this, a straightforward process should start from discovery, go through normalization and validation, and end with a tip report. The tip report goes through a triage process and finally enters the mitigation phase. For a tip to be practical, it’s crucial to act on it before the threats fully materialize. The timeliness of action varies depending on the type of tip. Some tips require immediate attention, while others can wait for months. Despite this, the company should provide guidelines to the teams responsible for managing tips.
Conclusion
The risks of researching on the dark web differ from other types of research. Legal, regulatory, and political risks must be considered when analyzing the dark web. Even if analysts and intelligence companies claim their work is black-box research, risks remain. Therefore, it's vital to establish policies and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) to minimize the risks to the analyst, their company, and their clients.
It's important to note that no specific target maturity score applies to all companies. Each company should evaluate what works best for its unique situation based on its budget, resources, and risk tolerance. The purpose of this blog is to help companies create a tailored list of variables that are relevant to their needs.
Resecurity provides intelligence services and can assist companies in defining an appropriate security model and developing policies and procedures for utilizing dark web intelligence to protect their products, services, customers, employees, and IP.

